Explore what B2B sales means, the different types, and the processes, tips, and best strategies that bring success.
Think of your sales team as your hunters. They provide for your business through acquisition of new business. A strong sales team is a necessity to starting, building, and maintaining a successful B2B organization.
Without further ado, let’s dive into B2B sales. I’ll first break down what B2B sales means, the different types, the process, and best strategies.

What is B2B sales?
Business to business (B2B) sales refers to business being conducted directly with another business. This is in contrast to the more commonly known business to consumer (B2C) model, which sells directly to the individual consumer. The B2B sales model simply means that it sells to other businesses.
B2B companies are now in virtually every industry. So, let’s take a deeper look at how B2B sales works.
Types of B2B sales
B2B sales are rather all encompassing. It can range from products being sold to businesses, products for manufacturers, even goods and services being sold from one business to another.
Here are a few examples:
Products for business
Remember The Office—the fictional documentary-style sitcom featuring a look into office lifestyle? Not only was the show hilarious, but it’s relevant to B2B. The fictional Dunder Mifflin and Michael Scott Paper Company exemplify B2B companies that sell paper products specifically to other businesses through prospecting leads over the phone, and closing business in person. Every business needs office supplies, such as computers, printers, and paper to be able to operate.
Products for manufacturers
When we think of products being sold to manufacturers, we can use a tire company as an example, selling its tires to a larger car manufacturer. Usually a car company will make some sort of deal to exclusively use one brand of tire with its latest models. While cars and tires working as B2B is just one example, there are plenty of other manufacturers who take advantage of B2B sales.
Business services
Business services refers to services companies provide other businesses.For instance,a consultancy firm being brought into a business to help on a project or a third-party designer has been freelanced to produce digital design for a company.
The B2B sales process
The B2B sales process can vary depending on the industry and the individual buyer, so it makes more sense to consider the customer buying cycle. Focusing on the customer, rather than the product will create a better opportunity to complete the sale. Let’s go through each step.
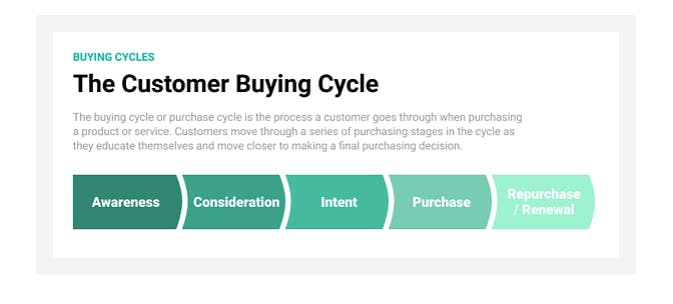
The customer buying cycle
Awareness:
Potential customers understand they have a problem that needs solving and begin to search for solutions.
Consideration:
At this point customers are considering their options, so you should be providing information explaining how your product or service can solve their problem.
Intent:
Decision-makers pit the various alternatives against each other—and whichever makes the most logical, emotional, or financial sense will be the one they end up choosing. Your sales team must do what they can to convince the prospect.
Purchase:
The customer has decided on the product they want to buy, and they buy it. But, your job isn’t done. It’s crucial to develop an ongoing relationship.
Repurchase/Renewal:
Your product has shown value and it continues to be an integral part of the customer’s business. This is where companies frequently find the biggest opportunities for increasing revenue.
B2B sales strategies for success
The recent shift to a customer-centric sales approach could not be more prevalent in B2B SaaS sales. As information about products and services are increasingly accessible to B2B buyers, they trust online information and product reviews more, and B2B salespeople less.
Rather than focusing on lead generation and closing deals, B2B sales reps need to establish customer trust.
Your B2B sales strategy should revolve around your customer’s needs. Your value proposition and a carefully crafted B2B marketing strategy are essential to B2B sales. Without them, you’re setting yourself up for churn.
1. Find the why
Understand your customer’s motivations and tailor your product’s value to their specific needs. This means you can’t use the same generic pitch for every customer. What’s the best way to do this? Research your customers, distribute surveys, and gather feedback from current customers, as well as potential customers as you build a relationship with them. Why should customers care? If they have a problem, you should present your product as a solution to that problem.
2. Refine your value proposition
Highlight your strengths and differentiators that set you apart from the competition. Motivate prospective customers to learn more. Your value proposition should be comprehensive, yet brief, and solve specific pain points for the customer. When possible, quantify value for your customers—provide a concrete and tangible ROI. And of course, continually reinforce your values to the customer.
More in-depth value proposition strategy can be found here.
3. Build relationships
Subscriptions are all about relationships. Customers are buying something once and then forgetting about; they are spending money on your product on a recurring basis. Whether it’s the beginning of the customer cycle, or throughout, you must build trust with your customers in order to successfully sell them your product/service, and to ensure retention and renewal. But how do you build trust? It begins with developing a rapport, asking questions and truly listening. You can connect with prospects on business-centric social media sites like LinkedIn. Make sure to follow-up and stay engaged. Show the customer you genuinely care.
4. Use social proof
Even in this day and age, word of mouth can make or break your organization. Social proof can stand between your sales team and their next sale. Customers want to know if your solution works for other organizations and what the sales and customer success process is like. Use case studies, testimonials, and even third-party review sites to your advantage.
B2B vs. B2C: where they differ
Imagine you’re an apple farmer with a large orchard. You have a decision to make between two business models. You can take your produce to the local farmers’ market, where you will likely sell small batches of your apples to a revolving door of customers, or you can partner with large outlets like supermarkets.
Selling to supermarkets will guarantee a purchase of large quantities of apples, but it also means providing a consistent supply at a fixed cost, as well as delivery. There’s a higher demand which leads to a higher upkeep, as well as hiring staff, and plenty of other costs associated with running a B2B business.
Selling your apples at your local farmers’ market is a very simplistic form of the B2C model. You’re taking the apples you’ve grown and selling them directly to people within your community. When you choose to sell your apples to the larger corporations, not only are you selling business to business, but you’re most likely taking on larger costs.
Let’s dive deeper on the discrepancies.
Price point
B2B sales come with a higher price point. It’s all part of the territory. You have to consider the buying and selling entities, and what they signify. In SaaS, you’re selling an essential piece of software, likeHubSpot, to another business. HubSpot is going to be this business' primary CRM and marketing platform.
Now depending on the number of users or data the CRM will hold, HubSpot will charge a premium for their service and platform. The purchasing business is buying something that it needs to solve a problem, and they’re willing to pay for it. Remember, your price is the exchange rate on the value you’re providing, so don’t skimp on it.
Analyzing and understanding data to know what your customers or target customers value will ensure price optimization, but it is an ongoing process.
B2C sales are transactional and are generally at a low price point that an individual can afford. Purchasing a car or a house comes with a greater price point, but we see most B2C sales happen between an organization and one person with decision-making ability.
Sales cycle
The B2B sales cycle will last longer, includes multiple touchpoints, and multiple stakeholders need to be considered throughout each step. As mentioned before, a B2C sale is very transactional and usually consists of one stakeholder. When making a purchase for an entire organization, not only do people able to make a purchasing decision have to be brought in, but also the people who will use said product/service.
Strategy
There’s an incredible amount of emotion that goes into B2C sales. Consider small businesses selling their product for the first time, or the first time someone buys a car. There is so much riding on that one transaction because it’s based more on emotion.
B2B sales can be rather cut and dry—strategic and rational. There is a strategy in place to ensure the sale happens, and again, there’s multiple stakeholders on each side to help move the buying process along.
Customer base
As mentioned in the beginning, B2B sales is entirely based upon selling to a business entity, rather than a single consumer. Identifying the correct buyer personas, and marketing to them correctly is crucial in B2B sales. You are providing a solution to an entire company, not just to a single consumer.
Final thoughts
B2B sales comes with a higher price point and a longer sales funnel. Understanding your customer personas, why they are in the market, and what problem they are trying to solve is key to successfully selling your product from your business to another. Not to mention knowing your value and developing a metric around it to help paint a clearer picture for your customers.



